VMware Data Recovery: Virtual Machine Backup and Recovery
 Virtualisation is a software technology that is transforming the IT landscape and in turn has created radical changes in computing. While most of today’s computing hardware was designed to only run one operating system at a time, virtualisation helps businesses overcome this limitation by allowing a single system to run several operating systems simultaneously, increasing its usage and flexibility. With virtualisation, users of VMware software save time, money and resources while optimising and rationalising their IT infrastructure. These advantages and savings explain the growing rate of virtualisation in business environments. While there are space saving, environmental and cost benefits to virtualisation and server consolidation, having all your data in one place can leave businesses vulnerable to experiencing substantial data loss.
Virtualisation is a software technology that is transforming the IT landscape and in turn has created radical changes in computing. While most of today’s computing hardware was designed to only run one operating system at a time, virtualisation helps businesses overcome this limitation by allowing a single system to run several operating systems simultaneously, increasing its usage and flexibility. With virtualisation, users of VMware software save time, money and resources while optimising and rationalising their IT infrastructure. These advantages and savings explain the growing rate of virtualisation in business environments. While there are space saving, environmental and cost benefits to virtualisation and server consolidation, having all your data in one place can leave businesses vulnerable to experiencing substantial data loss.VMware Data Recovery Appliance (vDR) – vDR is a virtual machine that facilitates backup and comes with vSphere Client plug-in. Works with ESX “Classic” and ESXi to backup VMs which allows for the backup of the VMs files. Support for advanced features such as compression of de-duplicated data. No network hit when used with shared storage. In the beta release there is no support for backing up individual files within the VM – and this feature will be only “experimentally” supported at the time of the vDR’s general availability. However, after the first backup – all subsequent backups are merely the delta changes within the virtual disk – using special change block tracking functionality available only in VMs with Hardware Level 7.
When VMware released vSphere, they also included a new product called VMware Data Recovery (VDR), which is their first entry into the virtual machine (VM) backup arena. Unlike VMware Consolidated Backup (VCB), which is an enabling technology and not an actual data backup product, VMware Data Recovery is a standalone product that creates hot backups of virtual machines to any virtual disk storage attached to an ESX/ESXi host, or to any NFS/CIFS network storage server or device and is not meant as a replacement for VMware Consolidated Backup.
The most common causes of VMware data loss are:
- Drive, RAID or iSCSI failure
- Deleted or corrupted virtual disks
- Accidentally reformatted RAID array
- Failed software SAN
- Reformatted or re-installed VMFS volumes
- VMFS file system corruption on ESX server
- Deleted files (virtual machine) on VMFS
- Internal VMDK or file corruption (SQL, Exchange and Oracle)
- Format and reinstall on VMFS volume
- Deleted files inside a virtual machine
- Corruption inside a virtual machine
Backup and restore of VMware virtual infrastructure, in my opinion, has never been very easy. VMware has never offered its own backup application, and no, VCB is NOT a backup application even though it is called “VMware Consolidated Backup”. VMware Consolidated Backup actually does not backup or restore anything. All VCB really does is to provide you access to the VMFS file system to allow you to use some other method of backup and restore on your virtual machines.
Prior to Data Recovery, every admin out there either;
- Wrote some scripts to use with VCB for backup
- Kept their traditional backup application running in each guest
- Used some interface where that allowed their traditional backup application to backup VMs using VCB
- Bought a virtualization-specific backup application like vRanger, esXpress, or Veeam Backup
What is VMware Data Recovery?
Data Recovery (or VDR) is the name of VMware’s new backup and recovery application. Contrary to the name, 50% of Data Recovery’s job is the backup of virtual machines (and 50% is “recovery”). Still, Data Recovery does a lot more than just backup and restore of virtual machines. Let’s look at a feature list:
- A real backup application with a GUI interface (unlike VCB)
- Integrated into vCenter
- Disk based backup and restore of VMware ESX virtual guest machines
- Easy deployment with initial setup wizard
- Restore of individual files from a guest VM or the entire image of a guest VM
- Wizard with workflow to create and schedule backup jobs
- Multiple restore points are displayed for each VM for easy restore
- Understands when VM guests are moved from one ESX host to another because of DRS, VMotion, or VMHA
- Full or incremental backups of guest VMs
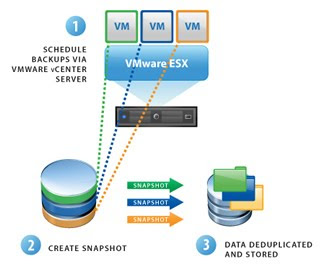
- De-duplication so that only changed data is actually backed up (not duplicate data). This way, you are able to maintain full point in time backups of each VM but only a fraction of the disk space, that would normally be required, is used
- Compatible with any storage that ESX supports- Fibre, iSCSI, NAS, or local
- Data Recovery is built on VMware Consolidated Backup (VCB) and, with vSphere, there is no more VCB, only Data Recovery
 VMware Data Recovery vs. Veeam Backup and Replication
VMware Data Recovery vs. Veeam Backup and ReplicationVMware's VMware Data Recovery product directly competes with several third-party vendors, including those from Veeam Software (Backup and Replication), PHD Virtual Technologies (esXpress) and Vizioncore Inc. (vRanger). However, VDR is a pretty basic, first-generation backup product and more suited for SMBs. While its basic functionality is similar to the other more mature products, it lacks the polish, advanced features and scalability that other products such as Veeam Backup and Replication offer. The chart below shows the major differences between the two products.
VMware Data Recovery vs. Veeam Backup and Replication | |
| VMware Data Recovery | Veeam Backup and Replication |
| Supports only vSphere ESX/ESXi hosts | Supports both VI3 and vSphere ESX/ESXi hosts |
| Does not support multiple vCenter Servers or standalone hosts not managed by a vCenter Server | Supports multiple vCenter Servers and standalone hosts |
| Supports only 100 virtual machines per backup appliance and 2 TB of source data | Supports 100-plus virtual machines and unlimited source data |
| Basic backup scheduling | Allows for very granular backup scheduling |
| File-level recovery is experimental and only supported on Windows systems | Mature file-level recovery for both Linux and Windows systems |
| Performs backups only, no replication | Performs both VM backups and replication |
| Performs block level, inline data deduplication | Performs block level, inline data deduplication |
It seems that a lot of people are getting confused as to where VDR fits in the grand scheme of things and how it differs from VMware Consolidated Backup (VCB).
In order to try and de-mystify this VMware have posted an article online explaining the various differences and how they see the different products “co-existing”. The article says “VDR will not replace VCB both products will co-exist. VMware Data Recovery is a separate product that is built on the VMware vStorage APIs for Data Protection(VADP).”
Things probably could have been made a little clearer…
How to install the VMware Data Recovery Appliance (vDR)
Prerequisites and assumptions:
- The user has the vSphere version 4 client and is attached to the new VCenter server.
- There is predetermined space on the SAN for backup storage.
- You have an open console to the vCenter server with the ISO connected to the CD drive with the Data Recovery install.
- The Data Recovery ISO is exported to a directory where you can access the files from the CD.
- An available routed IP accessible to the ESX servers.
- Access to DNS.
- A service account with full admin rights to servers and vCenter to use as the backup account.
- Network Share where backups will be written.
- Select an IP to use for you virtual data recovery appliance that is on a VLAN that is accessible to your ESX hosts.
- Open DNS administrator from Administrative Tools:
- Select new host A record:
- Enter the name of the Virtual Data Recovery appliance and the IP chosen and click the Add Host button. Then Close DNS manager and return the vSphere Client:
- Run the option from the splash screen to install Data Recovery:

- Click Next to continue:

- Click Next again:

- Check the circle to agree to the license terms and click Next to continue:

- Click Next again:

- Verify installation is complete and click Close:

- Launch the vSphere Client:

- Login with full admin credentials:
- Click on the VMware Data Recovery icon under Solutions and Applications from the Home screen:

- Click on File – Deploy OVF Template:

- Select the Deploy from file option and click Browse:

- In our example the file is in e:\iso\datarecovery\datarecovery\vmwaredatarecovery-ovf\, browse to the file, highlight and click open:

- Verify Information and click Next:

- Verify information and click Next:

- Name the appliance and select the folder in which it will be installed (for our example the name will be VDRAPP01 and the Folder will be Virtual Appliances):

- Select LUN to install appliance to (for our example CX4-LUN7) and click Next to continue:

- Select the cluster to install the appliance to (for our example New York Production):

- Select default network and VLAN and click next to continue (for our example 10.0.x.x network is chosen):

- Review information and click Finish to begin the install:
- Verify deployment is successful and click Close:

- Click on Home to return to the Home screen then choose hosts and clusters:


- Locate the virtual appliance and power it on through the console. When prompted click on Configure Network:

- This screen can also display DHCP networking information if your segment has DHCP on it.
- Answer No to the first prompt to use DHCP:

- Enter the IP Address X.X.X.X :
- Enter Netmask X.X.X.X :
- Enter Gateway X.X.X.X :
- Enter Primary and Secondary DNS X.X.X.X :
- When prompted for a proxy server answer NO:
- Review information and enter Y for Yes to accept:
- Be careful not to change the default TimeZone. We have experienced weird issues attributed to this.
- Restart the appliance and verify it boots then close the console:

VMware Data Recovery is a pre-installed Linux appliance which is imported into your vSphere cluster. VDR has GUI which will integrate with help of plugin onto vSphere client. VDR backup works by creating restore points for each of your VM virtual disks you wish to backup. Restore point is kind of full copy of virtual machine state at that current point in time when backup was created. VDR utilizes de-duplication on backup storage and it is very efficient to save backup storage space. VDR can use CIFS share or virtual disk as backup medium, that makes restoring data very quick. There is no support for tape backups.
FLR client works by mounting restore point into Windows VM as read only disk, from that disk you can restore invidual files or whole directories by copying them with standard Windows explorer.
To start using FRL download and copy vdrFileRestore.exe into your Windows VM, place it into some directory and make sure it is on PATH environment.
Make sure you have restore points available for you VM and execute vdrFileRestore.exe -a “IP or DNS name of your VDR” on Windows command line. FLR client uses unique BIOS id to identify which restore points it should make available for mounting for each VM.
FLR client will query which restore point in time you wish to mount
After you selected restore point FLR client will do some of its magic and backup of your Windows drives will show up in your VM as additional drives, FLR client will tell you which drive backup is available at which drive letter.
After you copied files you need, type “unmount” and press enter. This will close restore point mounts and FLR client will exit.
The VMware Data Recovery is an Agent-less disk based backup and recovery solution that can perform virtual machine or file level restores of Windows or Linux guess OS’s. It performs incremental backups plus data de-duplication and compression to save disk space. Data Recovery supports any disks that are accessible by the Data Recovery appliance. The disks could be in a VMFS volume or on shared disks such as NFS, DAS, iSCSI, Fiber, SMB\CIFS Shares.There's been a lot of talk about using VMware Data Recovery with ESX 4 and vSphere and what it does and doesn't do. We'll get the negatives out of the way first. vDR isn't a VCB replacement so if you still need a VCB proxy in your environment that will still need to be maintained. vDR doesn't write directly to tape. vDR's de-dupe technology is target based.. Therefore, you will experience disk space savings but all those redundant blocks will still be sent over the network.







 TechQuark is a mobile-friendly website. Simply bookmark
TechQuark is a mobile-friendly website. Simply bookmark 